The Phases Of Sleep In Adolescents

Restful sleep is one of the fundamental requirements for proper brain development in adolescents. Young people often underestimate the importance of complying with the hours of rest that are recommended for a balanced life.
The vitality of age seems to make up for the absence of adequate rest. However, the five stages of sleep in adolescents are as real as they are indispensable; especially considering that each phase responds to purely biological needs, corresponding to the stage of life that is being passed through.
Since the amount of rest that the body demands varies according to the biological cycle in which the person is, in adolescents this amount increases. In other words, a child or young person between 11 to 17 years old will need at least 9 to 10 hours of sleep a day.
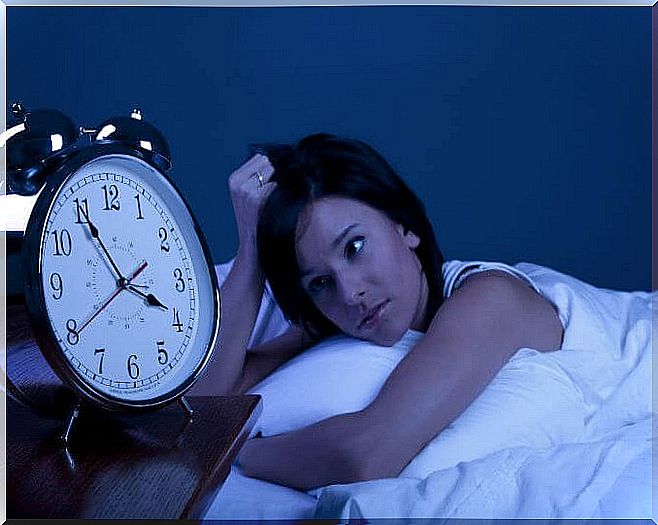
It is common for a teenager to have a hard time waking up in the morning. This is because your natural tendency will be to sleep through the cycle of sleep phases that your body needs.
Why fulfill the sleep phases in adolescents
The function of sleep, at any age, is to repair and give rest to the body and mind. When sleeping, a series of cellular regeneration processes are activated in order to obtain energy ; It is also during sleep that some hormones, such as growth hormones, can increase their production.
On the other hand, the mechanisms of memory, daytime attention and fixation of the contents or subjects learned are carried out during the hours of sleep.
Considering these reasons, it is understood that for adolescents, whose brain is completing its development, it is vital to take care of the quality and quantity of sleep. Lack of adequate rest can negatively influence psychological, physical and academic performance, and even behavior.

An adult can consciously control impulses and emotions. In adolescents, this is still part of a learning that requires, to be completed, respect for the biological rhythms of the body and mind.
What are the five stages of sleep in adolescents?
Sleep cycles have been described as having five phases since 1957. The model of WC Dement and N. Kleitman, who carried out their research using electroencephalograms, is still in force today. However, some details have been made with modern instrumentation.
In practice, each phase of sleep is known to last for around 100 minutes. It is also known that the five phases are repeated cyclically and continuously; These begin in a state of light sleep, go into deep sleep until reaching the REM state, also lighter, which prepares for awakening.
First phase
The numbness or transition phase comprises 5% of total sleep. This transition occurs between wakefulness and sleep and reappears in each repetition of the cycle. This is the phase known for registering Alpha waves, the same ones that occur in a moment of relaxation while awake.
Second stage
Here the disconnection with the environment begins to intensify. This enables the dream to gradually deepen; muscular and physiological activities decrease.
This is the light sleep that takes place after the first numbness. This phase constitutes approximately 50% of total sleep and gives rise to beta waves.

Third and fourth phase
Deep or delta sleep occurs in these phases. Within the sleep phases in adolescents, phases 3 and 4 are of great importance, like the rest, although it is here when the body’s recovery occurs most markedly.
Fifth phase
This is slow sleep, which occupies 25% of total sleep. In this phase, parasomnias or sleep disorders appear: sleepwalking, night terrors, nocturnal enuresis.
REM phase
This is phase 5, called ‘fast waves’ due to the characteristic of eye movements. The REM phase represents 20% of total sleep ; although the predominant waves are beta, that is, that has left deep sleep and delta waves; in this phase it is more difficult to wake up.
Before waking up, dreams and nightmares take place that are later remembered when opening the eyes; this phase is more extensive in children. This stage is considered essential for optimal brain development.
In summary, the sleep phases in adolescents must be respected for adequate mental and emotional development. The fact that adolescents sleep a lot is, without a doubt, a sign of health.